Social Sciences
Source: http://liu.brooklyn.libguides.com/c.php?g=138192&p=903530
citation count will only include the number of times the publication
was cited by articles from the journals that Scopus covers. Scopus does
not count citations from every journal published around the world, nor
does this method count citations from books, conference proceedings,
dissertations/theses, patents, technical reports or other types of
publications.
1. Scopus - Citation Analysis - LibGuides at Long Island University-Brooklyn
- Web Of Science - Citation Analysis Guide
Source: http://guides.lib.umich.edu/c.php?g=282982&p=1888178 Introduction The Web of Science database (composed of: Arts & Humanities Citation Index, Social Sciences Citation Index, and Science Citation Index...
- Glossary - Citation Analysis - Libguides At Long Island University-brooklyn
Source: http://liu.brooklyn.libguides.com/c.php?g=138192&p=903205 Useful Terms to Know Aggregate Cited Half Life: An indicator of the turnover rate for a body of work on a subject. Cited Half-Life: "The...
- Alternative Methods - Citation Analysis - Libguides At Long Island University-brooklyn
Source: http://liu.brooklyn.libguides.com/c.php?g=138192&p=903532 Introduction Certain disciplines, journals, and document types may not be well represented in the more traditional sources for...
- Google Scholar - Citation Analysis - Libguides At Long Island University-brooklyn
Source: http://liu.brooklyn.libguides.com/c.php?g=138192&p=903531 Introduction This section covers the use of Google Scholar for citation counts and identifies other applications that can be...
- Journal And Search Alerts
Source: http://www.libraries.iub.edu/index.php?pageId=3512 Journal and Search AlertsMany database vendors support alerting services for tables of content and subject and citation searches. In almost all cases, you must register for a (free) account...
Social Sciences
Scopus - Citation Analysis - LibGuides at Long Island University-Brooklyn
Source: http://liu.brooklyn.libguides.com/c.php?g=138192&p=903530
Introduction
Scopus is considered by many to be the
primary competitor to the Web of Science database for citation analysis
and journal ranking statistics.
The Scopus web site claims this database is the "largest abstract and
citation database of peer-reviewed literature and quality web sources
with smart tools to track, analyze and visualize research." It is
international in coverage and the Scopus interface is simple and
intuitive to use.
But ...
A citation search in Scopus is not a complete citation search:
primary competitor to the Web of Science database for citation analysis
and journal ranking statistics.
The Scopus web site claims this database is the "largest abstract and
citation database of peer-reviewed literature and quality web sources
with smart tools to track, analyze and visualize research." It is
international in coverage and the Scopus interface is simple and
intuitive to use.
But ...
A citation search in Scopus is not a complete citation search:
- Citation searching in Scopus only covers the titles include in this database.
- Since Scopus was only released in 2004 it does not have the long established record of Web of Science.
- Citation tracking in Scopus is only available for articles published from 1996 to the present.
- In the past, coverage was considered weak and
uneven in some areas such as physics, astronomy, math, sociology,
philosophy, theology, arts, and literature.This guide will show how to use Scopus to:- Find the Citation Count for a Publication
- Determine What Journal Articles Have Cited a Publication
- Get the Citation Count for a Specific Author
- Determine the Most Highly Cited Publications for an Author
- Determine the Most Highly Cited Articles for a Journal
- Set Up a Citation Alert for a Journal Article
Find the Citation Count for a Publication
- Access Scopus.
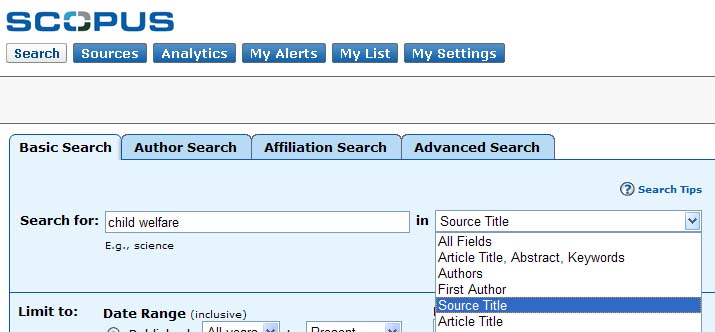
- Using the drop-down menu on the basic search option, select "Source
Title," enter the title of the journal, and click the search button. - If necessary, refine your results in order to include only the
journal you want. To do this select the box next to that title and click
the "limit to" button. - Scroll down to the list of results, check the box "select all," and
then click the "cited by" button immediately to the left of this check
box.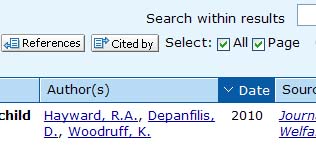
- The resulting list of articles are all of those which cited something in the particular journal title you searched.
citation count will only include the number of times the publication
was cited by articles from the journals that Scopus covers. Scopus does
not count citations from every journal published around the world, nor
does this method count citations from books, conference proceedings,
dissertations/theses, patents, technical reports or other types of
publications.
Determine What Journal Articles Have Cited a Publication
This section will demostrate how to find the number of times a particular article has been cited within the Scopus database.
- Enter the title of the article for your citation analysis using the
Basic Search. Use quotation marks around the title if you would like to
search the terms together. - Keep the default drop-down menu option "Article Title, Abstract, Keyword."
- For a more detailed search which includes the author(s) of this
article click on the link "add search field" and choose the appropriate
field to search from the drop-down menu. - The article will appear in a search results list and the column to
the far right will have the number of times this article has been cited
within Scopus. - Clicking on the number listed under the "Times cited" column will
take you to a list of the articles which cited the article you searched. - You may find it even more helpful to click on the "Abstracts + Refs"
button, located under the article title on the search results page.
This will show you the references used by this author for this article
along with those articles which cited the article in their own research.
Author Search
This search allows a user to search for detailed information on individual authors.
- Access Scopus.
- Select the Author Search tab and enter the author name and click
the search button. For the broadest search enter the last name and only
the first initial of the first name.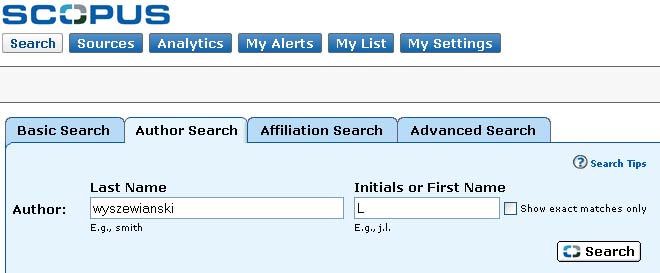
- The search results page will diplay all authors with citations in the Scopus database.
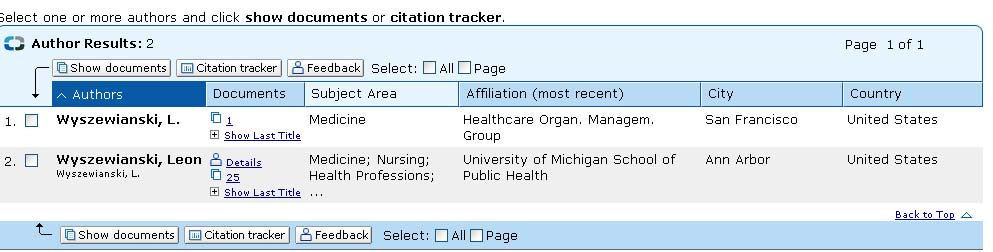
Be Aware: Look at the subject area and affiliation for each author listed. Multiple listings may in fact be referencing the same person. - Select one or more of the authors on the search results page by
checking the box next to the name or using the select all feature at the
top of the results list then click the Citation tracker button at the
top of the list to see a Citation Overview report.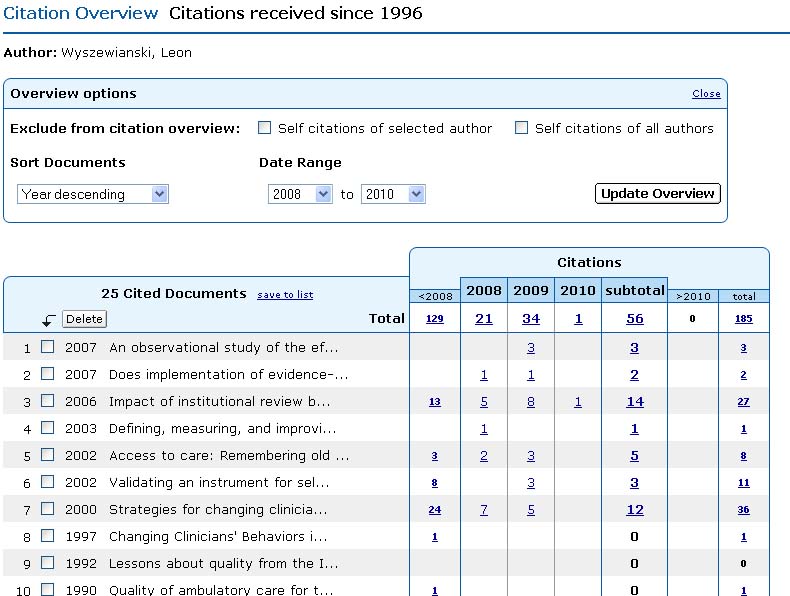
Determine the Most Highly Cited Papers for an Author
- Access Scopus.
- Follow the instructions above for Author Search to access the Citation Tracker report.
- Once on the Citation Overview screen choose to sort documents in
descending order from the drop-down menu in the Overview Options box.
Click the "Update Overview" button to resort the list of citations and
see which one has been cited the most.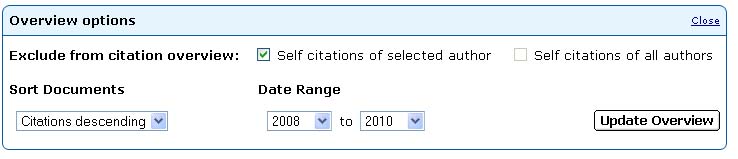
Determine the Most Highly Cited Papers for a Journal
This method can only be used for journals covered in Scopus; variant citations are not included in the citation determination.
1. Access Scopus.
2. Use the Basic Search box but select "Source Title" from the
dropdown menu, enter the full journal title and click the search button.
3. On
the results page, click on the column header "Cited by" at the far
right to sort the resulting articles by times cited. The article which
has been cited the most times will appear at the top of the list of
results.
1. Access Scopus.
2. Use the Basic Search box but select "Source Title" from the
dropdown menu, enter the full journal title and click the search button.
3. On
the results page, click on the column header "Cited by" at the far
right to sort the resulting articles by times cited. The article which
has been cited the most times will appear at the top of the list of
results.
Set Up a Citation Alert for a Journal Article
- Access Scopus.
- Login to your personal account using the "Sign In" link at the top of the page.
Citation
Alerts require registration (free); to register, click on the "Sign In"
link at the top of the page, in the left column, click on the
"Register" link and follow instructions. - Use the "Basic Search" to find the article.
- On the results list, click on the Abstracts + Ref button for the article.
- In the Cited by box at the right, click on the "E-mail Alert" link. Alerts are automatically set for one year.
- To edit or remove an alert, click on the "My Alerts" button at the
top of the page, just under the Scopus header; when your alerts are
displayed, click the "Edit" link to edit the alert or select the alert
and click the "Delete" button a specific alert from your lis
Attribution
The content on this page is borrowed with
permission from the University of Michigan Library and the Arizona
State University Library. You may access Michigan's Citation Analysis
guide here and ASU's guide here.
permission from the University of Michigan Library and the Arizona
State University Library. You may access Michigan's Citation Analysis
guide here and ASU's guide here.
1. Scopus - Citation Analysis - LibGuides at Long Island University-Brooklyn
- Web Of Science - Citation Analysis Guide
Source: http://guides.lib.umich.edu/c.php?g=282982&p=1888178 Introduction The Web of Science database (composed of: Arts & Humanities Citation Index, Social Sciences Citation Index, and Science Citation Index...
- Glossary - Citation Analysis - Libguides At Long Island University-brooklyn
Source: http://liu.brooklyn.libguides.com/c.php?g=138192&p=903205 Useful Terms to Know Aggregate Cited Half Life: An indicator of the turnover rate for a body of work on a subject. Cited Half-Life: "The...
- Alternative Methods - Citation Analysis - Libguides At Long Island University-brooklyn
Source: http://liu.brooklyn.libguides.com/c.php?g=138192&p=903532 Introduction Certain disciplines, journals, and document types may not be well represented in the more traditional sources for...
- Google Scholar - Citation Analysis - Libguides At Long Island University-brooklyn
Source: http://liu.brooklyn.libguides.com/c.php?g=138192&p=903531 Introduction This section covers the use of Google Scholar for citation counts and identifies other applications that can be...
- Journal And Search Alerts
Source: http://www.libraries.iub.edu/index.php?pageId=3512 Journal and Search AlertsMany database vendors support alerting services for tables of content and subject and citation searches. In almost all cases, you must register for a (free) account...
